What Makes Rolling Mill Rolls the Decisive Factor in Modern Steel and High-Wear Industrial Processing?
Introduction
Why do rolling lines with similar equipment configurations often deliver very different productivity, surface quality, and operating costs? In most cases, the answer lies in the selection and performance of rolling mill rolls.
Rolling mill rolls are not merely consumable components; they are precision-engineered tools that directly determine deformation efficiency, surface integrity, dimensional accuracy, and equipment stability. From hot rolling mill rolls exposed to extreme thermal shock, to cold rolling mill rolls operating under ultra-high contact pressure, and from heavy-duty forged rolls to auxiliary steel mill rollers, roll technology has evolved into a critical competitive factor for steelmakers and industrial OEMs.
This article provides a technical, application-driven analysis of rolling mill rolls, integrating material science, manufacturing processes, and real industrial demands, while highlighting how advanced cemented carbide roll solutions from TY HighTech address modern rolling challenges.
Why Rolling Mill Rolls Are Central to Rolling Process Performance
At their core, rolling mill rolls apply compressive force to plastically deform metal stock. In real production environments, rolls must simultaneously manage extreme mechanical loads, high friction and wear, thermal cycling, surface fatigue, and tight dimensional tolerances.
Any deficiency in roll material, structure, or surface integrity immediately leads to increased scrap rates, surface defects, frequent roll changes, unplanned downtime, and higher operating costs. This is why modern rolling operations treat rolling mill rolls as strategic process assets rather than standard spare parts.
Classification of Rolling Mill Rolls by Application
Hot Rolling Mill Rolls
Hot rolling mill rolls operate at temperatures that can exceed 1,000 °C. Their primary challenge is thermal fatigue resistance rather than hardness alone.
Key performance requirements:
- Resistance to fire cracking
- Stable hot hardness
- High thermal conductivity
- Oxidation resistance
- Structural integrity under thermal cycling
Common materials: high-chromium cast iron, adamite steel, and high-speed steel composite rolls. These rolls are widely used in roughing mills, finishing stands, plate mills, and bar and wire rod lines.
Cold Rolling Mill Rolls
Cold rolling mill rolls operate at ambient temperature but face extremely high contact pressure and surface finish requirements.
Technical characteristics:
- Surface hardness above HRC 60
- Surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.2 μm
- High resistance to contact fatigue
- Minimal elastic deformation
Cold rolling mill rolls are critical for producing automotive body sheets, stainless steel strips, electrical steel, and electronics-grade materials.
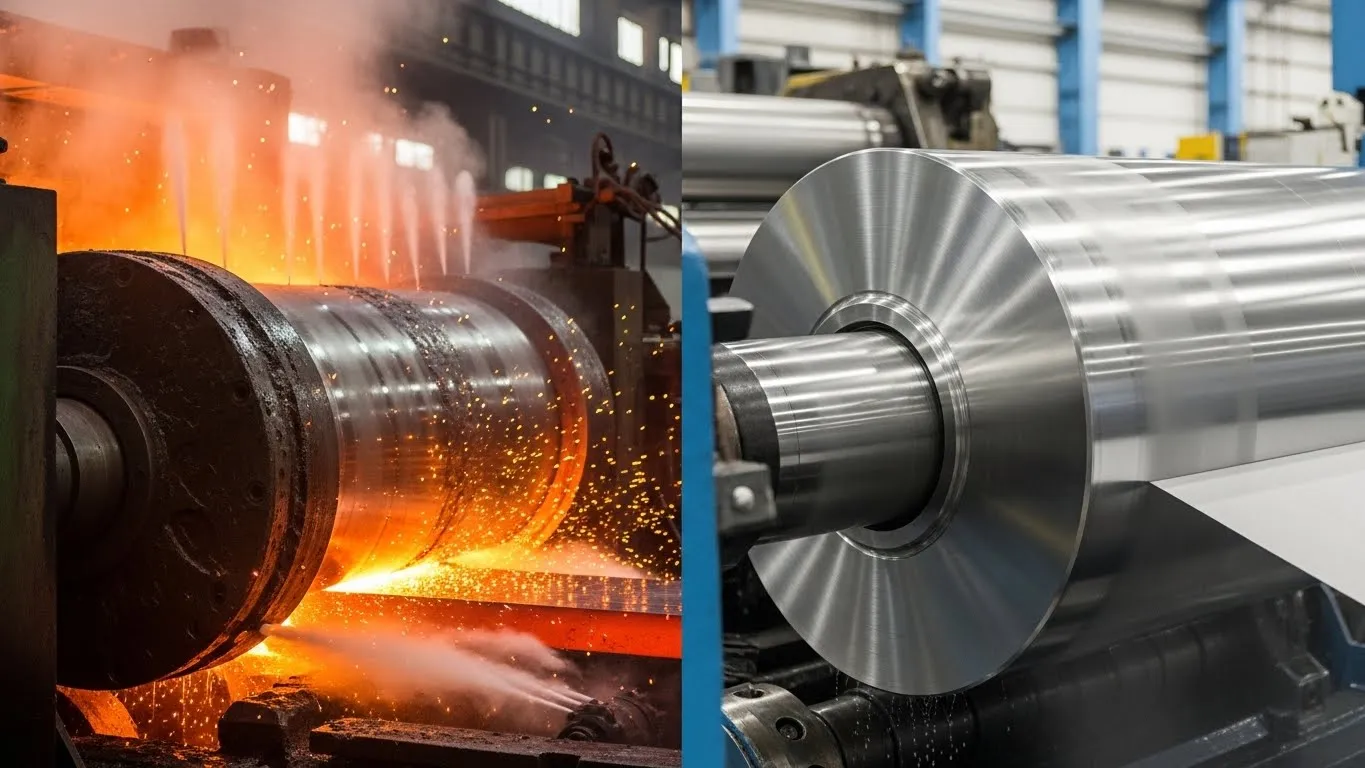

Forged Rolls
Forged rolls are manufactured through controlled forging and heat treatment, resulting in a dense and uniform microstructure.
Advantages include:
- Superior fatigue resistance
- High impact toughness
- Reduced internal defects
- Extended service life
Forged rolls are commonly used as backup rolls, work rolls in high-load stands, and reversing mills.
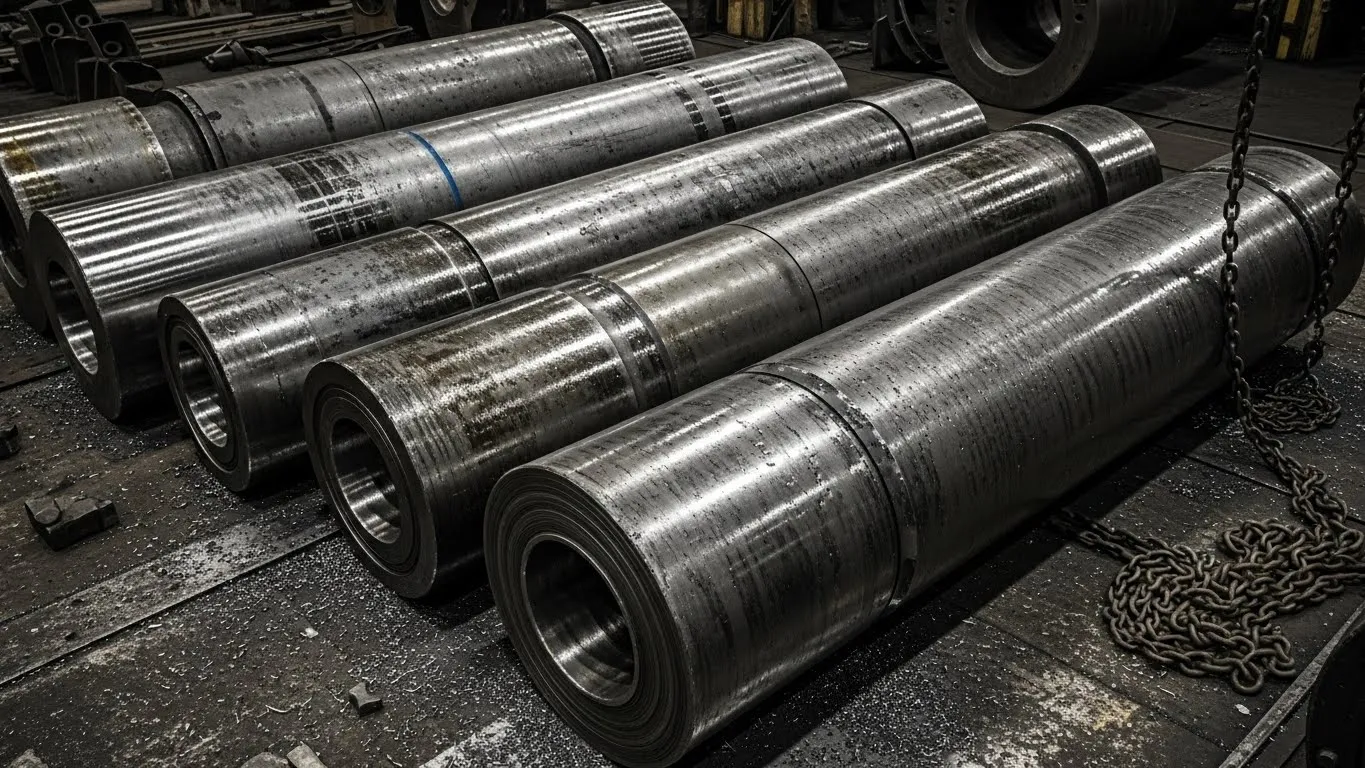

Steel Mill Rollers
Steel mill rollers support strip transport, guidance, and tension control. They are used in run-out tables, entry and exit guides, furnace conveyors, and tension leveling systems.
Inferior steel mill rollers can cause misalignment, vibration, and surface damage, negatively affecting final product quality even when premium work rolls are used.
How Material Selection Determines Roll Performance
Limitations of Traditional Steel Rolls
Conventional alloy steel and cast iron rolls often suffer from rapid wear, diameter loss, frequent grinding, and inconsistent surface quality, particularly in high-speed continuous rolling lines.
Cemented Carbide Rolls
Cemented carbide rolls represent a major technological advancement in rolling mill roll design.
Material advantages:
- Ultra-high hardness (HRA 88–92)
- Exceptional wear resistance
- Minimal diameter reduction
- Stable surface finish throughout service life
TY HighTech provides cemented carbide rollers engineered for cold rolling of stainless steel, precision strip mills, electronics equipment, and high-speed wire and rod rolling.
Reference: https://tyhightech.com/product/Cemented-Carbide-Roller
Manufacturing Technologies for Advanced Rolling Mill Rolls
Powder Metallurgy
Used for cemented carbide rolls, enabling precise control of carbide grain size, binder distribution, and wear resistance.
Forging and Heat Treatment
Optimizes grain flow, hardness gradients, and core toughness for high-load applications.
Precision Grinding and Surface Engineering
Ensures micron-level dimensional accuracy, customized surface roughness, and crown profile control.
TY HighTech integrates material science with application-driven design to deliver consistent roll performance.
Technical overview: https://tyhightech.com/about-us
Common Failure Modes of Rolling Mill Rolls
- Surface spalling caused by contact fatigue
- Fire cracking due to thermal shock
- Excessive wear from insufficient hardness
- Strip marking from surface damage or contamination
- Roll fracture caused by internal defects or overload
Advanced materials such as cemented carbide significantly reduce these risks.
Hot vs Cold Rolling Mill Rolls: Technical Comparison
- Hot rolling rolls operate under high thermal stress and moderate surface finish requirements
- Cold rolling rolls operate under extreme contact pressure and require ultra-high surface quality
- Wear mechanisms differ significantly between the two processes
Why Cemented Carbide Rolls Are Gaining Global Adoption
Industrial users increasingly select cemented carbide rolls because they extend roll life, reduce roll changes, improve dimensional consistency, lower total cost of ownership, and support automated high-speed rolling lines.
Applications Beyond Traditional Steel Rolling
TY HighTech roll solutions are also applied in electronics manufacturing, precision glass forming, non-ferrous rolling lines, and high-wear industrial machinery.
FAQs About Rolling Mill Rolls
1. Why do cold rolling mill rolls require higher surface quality?
Surface defects are directly transferred to the finished strip during cold rolling.
2. Are forged rolls always better than cast rolls?
Forged rolls offer superior integrity, but cast rolls may be suitable for lower-load applications.
3. How do cemented carbide rolls reduce operating costs?
They reduce downtime, grinding frequency, and replacement costs.
4. What industries benefit most from advanced roll materials?
Steel processing, electronics, glass manufacturing, and high-wear industrial sectors.
5. Can steel mill rollers affect final product quality?
Yes. Poor-quality rollers can cause misalignment, vibration, and surface damage.
6. How do I choose a reliable roll supplier?
Evaluate material expertise, application experience, customization capability, and technical support.
Conclusion
Rolling mill rolls engineered with advanced materials, precise manufacturing, and application-driven design are the defining factor in modern rolling operations. From hot rolling to cold rolling, forged rolls to steel mill rollers, correct roll selection directly determines productivity and quality.
With its focus on cemented carbide technology and industrial customization, TY HighTech provides roll solutions aligned with the evolving demands of global rolling industries.
Contact TY HighTech
Email: [email protected]
Tel: +86-199-7311-3715
Contact page: https://tyhightech.com/contact-us
Related product categories
- carbide roller rings for stainless steel production
- China carbide roll rings for wire rod production
- wear-resistant roller rings for plate mills
- corrosion-resistant carbide rolls for seamless tube mills
- long-life roller rings for bar mills
- wear-resistant rolls for sale
- comparison of carbide roll rings and steel roll rings Italy
- high grinding tungsten carbide for engraving
- cemented carbide roller mill for finishing
- solid tungsten carbide rod
- mill tools
- Carbide CNC Endmill
 EN
EN UR
UR ru
ru bn
bn ar
ar ky
ky th
th fil
fil vi
vi ms
ms tr
tr ro
ro pt
pt es
es af
af fa
fa uk
uk nl
nl pl
pl fr
fr de
de

